Osteochondrosis of the chest is an inflammatory disease accompanied by the development of pathological processes in the intervertebral discs. Complications of the disease include the appearance of protrusion and degenerative changes in the adjacent tissues. Osteochondrosis is difficult to identify due to the "masking" of symptoms such as gastritis, heart disease or stomach ulcer.
Features of the disease
Osteochondrosis of the chest is a complex of disorders in the intervertebral discs. They shrink and gradually lose their properties. This leads to pinching of the nerves.
According to ICD-10, this disease is in the "Dorsopathy" group under code M-42, localization.
In the early stage of the disease, examination and treatment can be prescribed by a local doctor. If the disease is advanced, the patient is referred to a highly qualified specialist (neurologist). Often, the professional massage therapist relieves the patient from the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis. In case of complications, you cannot do without the help of a surgeon.
reasons
Most often, the pathology manifests itself in the elderly. But in recent years, osteochondrosis of the chest more often affects young patients.

The development of the disease is provoked by various reasons:
- excessive physical activity;
- work involving heavy lifting;
- prolonged forced uncomfortable positions;
- congenital curvature of the spine and acquired postural disorders;
- improper diet;
- Overweight;
- age-related changes;
- metabolic problems.
Other factors for the development of osteochondrosis of the chest include chronic diseases and hereditary factors. To avoid pathology and possible complications, you need to get rid of the cause. Specialists claim that this problem in most cases is the result of an unhealthy lifestyle.
Degrees and symptoms
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is characterized by special symptoms. The patient suffers from muscle spasms and intercostal neuralgia. The pain can be localized in one place in the chest and then quickly spread to the chest. Because of this, a person has difficulty breathing, he must sit or lie only in a certain position.
The pain increases when turning the head, moving the neck, raising the arms and bending over. Any movement of the neck causes discomfort (especially at night). Painful contraction of the muscles of the shoulder girdle and lower back is possible.
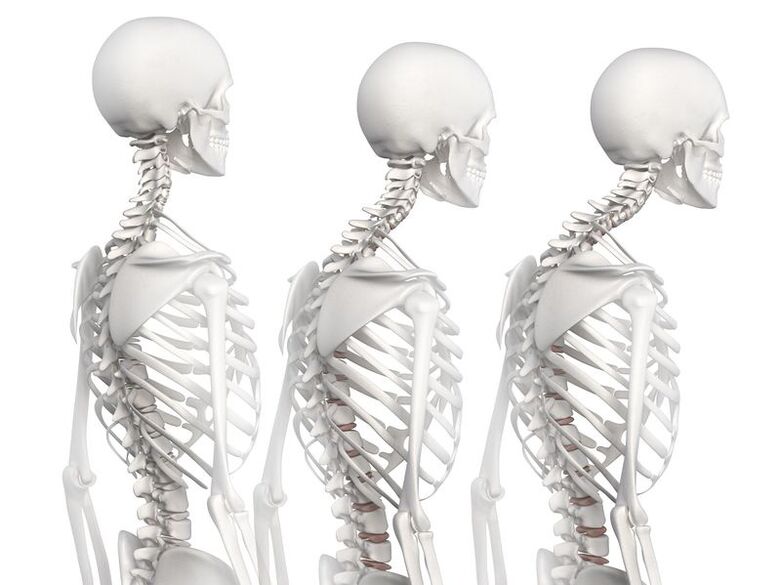
Taking into account the level of deformation of the intervertebral discs, the following degrees of development are distinguished:
First degree
At the first stage, the elasticity (stiffness) of the discs and their height is reduced. Possible manifestation of bulging (bulging) of the annulus fibrosus (hard shell for the semi-fluid nucleus). The cartilage tissue of the vertebrae becomes denser. Pain in the form of "lumbago" is likely during sudden movements or after staying in one position for a long time.
Dorsago- a characteristic symptom of this stage. It manifests itself in sharp, sudden pain in the chest. It often occurs when a person stands up (difficulty breathing).
Dorsalgia- mild, mild pain. It comes on gradually and usually lasts 2 to 3 weeks. It may worsen with sudden bending or after physical exertion. Dorsalgia is accompanied by muscle tension and restriction of movement. The pain subsides after a short walk.
Neurological symptoms are also identified at this stage:
- feeling of "pins and needles" on the surface of the legs, abdomen and chest;
- numbness or tingling in certain areas of the skin;
- dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Second major
There is a further decrease in the height and elasticity of the intervertebral discs. The thoracic spine becomes unstable, cracks appear in the fibrous ring.
Painful sensations:
- in the chest after overload or during physical exertion;
- in upper back;
- when raising the arms up;
- during breathing (inhalation and exhalation).
Phantom pains in the heart area and intestinal dysfunction are also possible.
Third degree
The formation of the intervertebral hernia continues. Pain is felt in the abdomen and back, intercostal neuralgia (may increase with inhalation, sudden movements and coughing).
One of the symptoms of osteochondrosis is a cough. The general mobility of the spine decreases, the diaphragm is compressed and a lack of air is felt. A strong dry cough is especially dangerous because the vertebral artery is located in the neck. If it gets squeezed, there is a risk of ischemia and stroke.
Fourth degree
In the fourth stage, the intervertebral discs cease to function as shock absorbers. The spine loses mobility. Possible pinching of blood vessels and nerves. Bone tissue is susceptible to destruction.
Diagnosis
Osteochondrosis of the chest is difficult to diagnose because it has "camouflage" (similar) symptoms of other diseases.
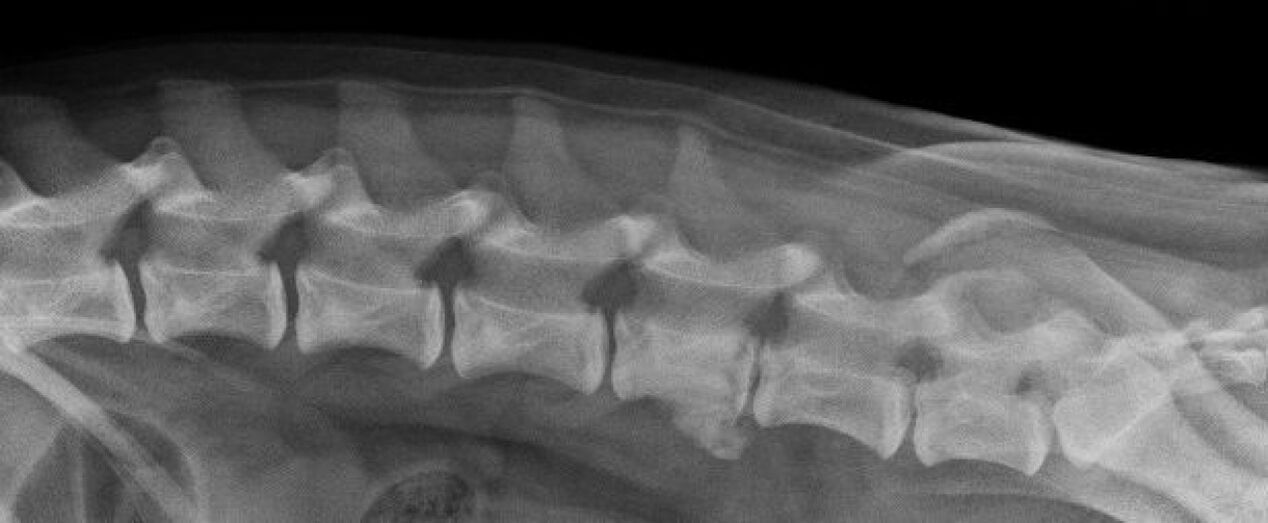
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to conduct a number of tests:
- ultrasound;
- Roentgen;
- MRI;
- blood analysis.
Traditional treatment
To eliminate pain and inflammation in the chest, drug treatment is used. To relieve pain during an exacerbation, injections are given into a vein or intramuscularly. Treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out with the help of drugs containing an enzyme of plant origin - papain. This substance helps to improve the structure of cartilage tissue.
- Chondroprotectors. This is a group of drugs used to repair joint cartilage. The basis of most products are the active substances - glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate.
- Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants.Medicines that weaken muscle tone. By acting on the receptors in this way, they relieve the unhealthy muscle tension that leads to pain and spasms.
- Pain relievers.It reduces the symptoms of the disease - inflammation and pain. The principle of action of such drugs is to block the synthesis of certain enzymes.
- Vitamin therapy.Most often, vitamins A, B, D, C, E are prescribed, which restore cartilage tissue, strengthen the immune system and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Massage.Patients with this disease must undergo a course of restorative massage at least 2 times a year. During an exacerbation of the disease, the procedure is usually not performed. This procedure improves blood circulation, relieves fatigue and muscle pain, strengthens muscle tone. The session lasts a quarter of an hour, the duration of the course is 11-16 procedures.
- Reflexology.Special techniques work on acupuncture points. In combination with other methods, the method is effective.
- Exercise therapy.The disease is characterized by an underdeveloped muscle corset and joint stiffness. A specially selected set of exercises (physical therapy) will help eliminate these manifestations. The first classes should be held under the supervision of an experienced instructor, after which gymnastics is performed independently. Regular training is very important.
Treatment at home
Home methods are used only as additional means to the main conservative therapy:
- Eating
To improve the condition, you need to eat properly: 6-7 meals a day, reducing the amount of salt intake, introducing vegetables and fruits, natural chondroprotectors (jelly, jellied meat) into the diet. In addition, it is important to lead an active lifestyle, avoiding any kind of overload.
- Berry tea
Breast osteochondrosis can be reduced by systematically drinking berry tea as well as wild strawberry leaf tea. Place a tablespoon of the plant in a glass, add hot water and let it steep. It is recommended to drink at least two glasses of this drink per day (after meals).
- Potatoes and honey
Grated potatoes mixed with liquid honey can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. The composition is applied to the painful part for 30 minutes.

Control your weight, increase the body's defenses and include a lot of plant foods in your menu. In compliance with the presented recommendations, the therapeutic effect occurs faster, the risk of complications and remissions decreases.





































